一、introduction
兼容性前缀
| prefix(前缀) | browser |
|---|---|
| -webkit | chrome/safari |
| -moz | firefox |
| -ms | IE |
| -o | opera |
1.历史
更新迭代,兼容性 —- 加不加前缀
div {
border-radius: ;
-webkit-border-radius: ;
-o-border-radius: ;
-moz-border-radius: ;
}兼容性手册网站
2.处理器
预处理器:pre-processor
less/sass cssNext 插件
利用 sass 工具编辑(遵循人家的语法):减少人工时间
sass 演示
div {
span {
}
}$font-stack: arial, ...;
#mysituation-color: #444;
div {
span {
color: #mysituation-color;
}
p {
font: 100% $font-stack;
}
}
#only {
&.demo {
color: $mysituation-color;
}
}后处理器:post-processor
CSS 自动补足前缀插件(基于 caniuse 网站)autoprefixer
后处理器需要在其环境内编写
优点:如果有一天,属性可以再各大浏览器应用,不需要加前缀,那么我们写的代码本身就符合规范了。可维护性好。而 sass less 不能。
3.怎么用
postCss + 插件(充分体现扩展性,200 多个)
postCss 并不能划分成什么处理器,要加上插件才能变成相应的处理器
用 js 实现 css 抽象的语法树,AST(abstract Syntax Tree),剩下的事情留给后人来做
后处理器好处:
如果浏览器都实现兼容了,用不到兼容了,就可以不用后处理器了,利于维护代码,升级。预处理器办不到。
4.CSS3 进化到编程化:cssNext
:root {
--headline-color: #333;
}
@custom-selector: --headline h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6
: --headline {
color: var(--headline-color);
}cssNext 用来实现一些未来的标准的(未完全在各大浏览器)
二、选择器
打开格局视野,不要故步自封,不要排斥知识,充分包容各种知识
1.关系型选择器模式(不常用)
E+F:下一个满足条件的兄弟元素节点
<div>div</div>
<p>1</p>
<p>2</p>
<p>3</p>
<p>4</p>div + p {
/*选择div兄弟下一个兄弟节点,叫p*/
background-color: red;
}E~F:下一堆满足条件的兄弟元素节点
<div>div</div>
<span class="demo">234</span>
<p class="demo">1</p>
<p>2</p>
<p>3</p>div ~ p {
background-color: green;
}2.属性选择器(不常用)
复习属性选择器:
<div class="demo" data="a" > data</div > <div > </div > div[data] {
background-color: red;
}1.小破浪
属性名是 data,属性值里面有独立 a 的元素
<div data="a">1</div>
<div data="b">2</div>
<div data="a b">3</div>
<div data="aa b c">4</div>div[data~="a"] {
background-color: red;
}
/*1,3变色*/2.小竖线
以 a 开头或者以 a-开头
div[class|="a"] {
background-color: red;
}<div class="a">1</div>
<div class="a-test">2</div>
<div class="b-test">3</div>3.^以…开头,$以…结尾,*存在
div[class$="a"] {
background-color: red;
}<div class="a">1</div>
<div class="a-test">2</div>
<div class="b-test">4</div>3.伪元素选择器(不常用)
before,after 一个两个冒号都可,但是接下来的两个必须两个冒号
1.placeholder
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入用户名" > input::placeholder {
color: green; /*只能改变字体颜色*/
}2.selection
<div>成哥很帅</div>
<div>邓哥也很帅</div>div:nth-of-type(1)::selection {
/*只能用这三种属性*/
/*color*/
/*background-color: */
/*text-shadow: 阴影*/
text-shadow: 3px 5px black;
color: #fff;
background-color: #fcc;
/*实现选中变色*/
}
div:nth-of-type(2)::selection {
color: yellow;
background-color: green;
}user-select: none 不让选中;DEMO
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
span::selection {
background-color: green;
color: yellow;
}
</style>
<body>
名下痴汉tid梦,也从大家的视线中消失了。<span>老</span>dengxu是一位非Two将打败过dengxu作为自己的主要战绩吹了很久。
后来dengxu海归追梦,也从大家的视线中消失了。<span>邓</span>dengxu是一位非常有实大家的视线中消失了。<span>虚</span>dengxu是一位非常有实
<span>弱</span>名下痴汉tidesof
</body>
</html>DEMO
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
p {
display: inline-block;
width: 200px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
p::first-letter {
font-size: 30px;
}
p::first-line {
color: green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>沙拉酱擦参考手册是空的充电口穿梭在考虑到开始做看大V南京市的计算机</p>
<input type="text" name="a" readonly /><span>dg</span>
<input type="text" name="a" read-write /><span>ds</span>
</body>
</html>4.伪类选择器
1.not(s)
案例
<div class="demo">1</div>
<div class="demo">2</div>
<div class="test">3</div>
<div>4</div>div:not([class]) {
background-color: red;
}实际开发类似需求—-移动端列表页:除了最后一个都要加上一条横线
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
ul{
width: 300px;
border:1px solid #999;
}
li{
height: 50px;
margin: 0 5px;
/*border-bottom: 1px solid black;*/
}
li:not(:last-of-type){
border-bottom: 1px solid black;
}
<ul>
<li>content</li>
<li>content</li>
<li>content</li>
<li>content</li>
<li>content</li>
<li>content</li>
<li>content</li>
</ul>2.root 和 html 地位相等
区別:
1.root:根标签选择器 html xml
2.html:根标签
3.root 包含 html
用法:
:root{background-color}3.target
含义
被标记成锚点之后–location.hash=×××
案例:可点击创造锚点
<a href="#box1">box1</a>
<a href="#box2">box2</a>
<div id="box1">1</div>
<div id="box2">2</div>div:target {
border: 1px solid red;
}DEMO
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>finish js</title>
<style>
*{
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
list-style: none;
}
body{
height: 2000px;
}
a{
position: fixed;
top:0;
}
.item{
position: absolute;
top:1000px;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: red;
}
#item1{
top:500px;
}
#item2{
top:1000px;
}
#item3{
top:1500px;
}
.item:target{
background: green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="#item1" style="left:200px">click1</a>
<a href="#item2" style="left:300px">click2</a>
<a href="#item3" style="left:400px">click3</a>
<div id="item1" class="item">1</div>
<div id="item2" class="item">2</div>
<div id="item3" class="item">3</div>
</body>
</html小项目:三个 a 标签控制页面背景颜色
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
/*实现div=屏幕的高度 */
:root,
body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
height: 100%;
}
#red,
#green,
#gray {
height: 100%;
width: 100%;
}
#red {
background-color: #f20;
}
#green {
background-color: green;
}
#gray {
background-color: gray;
}
div[id]:not(:target) {
display: none;
}
div.button-wrapper {
position: absolute;
width: 600px;
top: 400px;
}
div.button-wrapper a {
text-decoration: none;
color: #fff;
background-color: #fcc;
font-size: 30px;
border-radius: 3px;
margin: 0 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="button-wrapper">
<a href="#red" class="bgred">red</a>
<a href="#green" class="bggreen">green</a>
<a href="#gray" class="bggray">gray</a>
</div>
<div id="red"></div>
<div id="green"></div>
<div id="gray"></div>
</body>
</html>4.其他伪类选择器(此部分都考虑其他元素的影响)
受其他元素的影响,父子级,不出常用
1.first-child
<div>
<p>1</p>
<p>2</p>
<p>3</p>
</div>/*伪类选择器是被选择元素的状态*/
p:first-child {
background-color: red;
}<p>1</p>
<div>
<p>1</p>
<p>2</p>
<p>3</p>
</div>是不是 first-child,不只看是 p 里面的第一个,要看父级下面的第一个
<div>
<span>0</span>
<p>1</p>
<p>2</p>
<p>3</p>
</div>2.last-child
<div>
<p>1</p>
<p>2</p>
<p>3</p>
</div>
<p>4</p>
<!-- last-child:只要是最后一个儿子,就可,即14 -->3.only-child
span:only-child {
background-color: aqua;
}
div:only-child {
background-color: blueviolet;
}<div>
<span>0</span>
<p>1</p>
</div>DEMO
nth-child(n)<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
/*实现div=屏幕的高度 */
:root,
body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
height: 100%;
}
#red,
#green,
#gray {
height: 100%;
width: 100%;
}
#red {
background-color: #f20;
}
#green {
background-color: green;
}
#gray {
background-color: gray;
}
div[id]:not(:target) {
display: none;
}
div.button-wrapper {
position: absolute;
width: 600px;
top: 400px;
}
div.button-wrapper a {
text-decoration: none;
color: #fff;
background-color: #fcc;
font-size: 30px;
border-radius: 3px;
margin: 0 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="button-wrapper">
<a href="#red" class="bgred">red</a>
<a href="#green" class="bggreen">green</a>
<a href="#gray" class="bggray">gray</a>
</div>
<div id="red"></div>
<div id="green"></div>
<div id="gray"></div>
</body>
</html>4.nth-child()
CSS 从 1 开始,n 是从 0 开始 odd 奇数 even 偶数
p:nth-child(2n) {
background-color: blueviolet;
}<div>
<p>1</p>
<p>2</p>
<p>3</p>
<p>4</p>
<p>5</p>
</div>5.nth-last-child(n)
倒着数
5.其他伪类选择器(不受其他影响)
不受其他影响,常用
1.first-of-type
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
<li>4</li>
<li>5</li>
<li>6</li>
</ul>
<li>1</li>li:first-of-type {
background-color: aqua;
}这一类型里面是的第一个
2.last-of-type
3.only-of-type
<div>
<span>0</span>
<p>1</p>
<!-- <p>2</p>不是特有的了 -->
</div>p:only-of-type {
background-color: aqua;
}4.nth-of-type(n)常用
<div>
<span>0</span
><!-- 注意这一行 -->
<p>1</p>
<p>2</p>
<p>3</p>
<p>4</p>
<p>5</p>
<!-- <p>2</p>不是特有的了 -->
</div>p:nth-of-type(n+2){从第二个开始查
background-color: aqua;
}5.nth-of-last-type(n)
与前一个相反
6.剩下的伪类选择器
1.empty:必须元素是空的,才叫 empty
<div><span>123</span></div>
<div></div>
<div>234</div>
<div><!--sda--></div>
<!--注释也算节点-->div:empty {
border: 1px solid black;
height: 100px;
}2.checked
<label> 一个小惊喜<input type="checkbox" /><span></span> </label>input:checked {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
}DEMO 处理简单交互
<style>
input:checked + span {
background-color: green;
}
input:checked + span::after {
content: "隔壁老王 电话xxx,请务必小心刑事";
color: #fff;
}
</style>
<label>
一个小惊喜
<input type="checkbox" />
<span></span>
</label>3.enable
<input type="text" /> <input type="text" disabled />input:enabled {
background: green;
}
input:disabled {
border: 1px solid #f20;
background-color: #fcc;
box-shadow: 1px 2px 3px #f20;
}4.disable
5.read-only
input:read-only{
color:chartreuse;
}
<input type="text">
<input type="text" readonly value="你只能瞅着,干不了别的">6.read-write
选项卡
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
list-style: none;
}
.wrapper {
position: relative;
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
border: 1px solid black;
text-align: center;
margin: 0 auto; /*居中*/
}
.wrapper input {
width: 30px;
height: 30px;
}
/*.wrapper div和.wrapper实现三个小圆点在一行展示,块级元素。*/
/*.wrapper div相对于.wrapper定位:top,left*/
.wrapper div {
position: absolute;
top: 30px;
left: 0;
width: 400px;
height: 370px;
display: none; /*先都是none,选中那个那个变成block*/
text-align: center;
line-height: 370px;
font-size: 30px;
color: #fff;
}
.wrapper div:nth-of-type(1) {
background-color: red;
}
.wrapper div:nth-of-type(2) {
background-color: green;
}
.wrapper div:nth-of-type(3) {
background-color: blue;
}
input:checked + div {
/*input:checked + div{ 不要有空格,否则错误*/
display: block;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<input type="radio" name="a" checked />
<div>a</div>
<input type="radio" name="a" />
<div>b</div>
<input type="radio" name="a" />
<div>c</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>手风琴
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>原生js手风琴特效</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
ul,
li {
list-style: none;
}
.box {
width: 1050px;
height: 300px;
margin: 100px auto;
overflow: hidden;
}
.accordion li {
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 300px;
color: #000;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<ul class="accordion">
<li style="background: #f99;">1</li>
<li style="background: #9ff;">2</li>
<li style="background: #f9f;">3</li>
<li style="background: #9f9;">4</li>
<li style="background: blue;">5</li>
<li style="width:450px;background: yellow;">6</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
function accordion() {
var oBox = document.querySelector(".box");
var accordion = oBox.querySelector(".accordion");
var oList = accordion.getElementsByTagName("li");
var i = 0;
var timer = null;
//console.log(oList.length);
for (var i = 0; i < oList.length; i++) {
oList[i].index = i;
oList[i].onmouseover = function () {
var index = this.index;
if (timer) {
clearInterval(timer);
}
timer = setInterval(function () {
var iWidth = oBox.offsetWidth; //盒子的总宽度
//console.log(iWidth); 1050
for (var i = 0; i < oList.length; i++) {
if (index != oList[i].index) {
//设定速度
var speed = (100 - oList[i].offsetWidth) / 5;
speed = speed > 0 ? Math.ceil(speed) : Math.floor(speed);
oList[i].style.width = oList[i].offsetWidth + speed + "px";
iWidth -= oList[i].offsetWidth;
}
oList[index].style.width = iWidth + "px";
}
}, 30);
};
}
}
accordion();
</script>
</body>
</html><!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
font-size: 12px;
list-style: none;
}
.menu {
margin: 50px auto;
width: 210px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
}
.menu p {
height: 25px;
line-height: 25px;
background: #eee;
font-weight: bold;
border-bottom: 1px solid #ccc;
text-indent: 20px;
cursor: pointer;
}
.menu div ul {
display: none;
}
.menu li {
height: 24px;
line-height: 24px;
text-indent: 20px;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload = function () {
var menu = document.getElementById("menu");
var ps = menu.getElementsByTagName("p");
var uls = menu.getElementsByTagName("ul");
for (var i in ps) {
ps[i].id = i;
ps[i].onclick = function () {
var u = uls[this.id];
if (u.style.display == "block") {
u.style.display = "none";
} else {
u.style.display = "block";
}
};
}
};
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="menu" id="menu">
<div>
<p>Web前端</p>
<ul style="display:block">
<li>JavaScript</li>
<li>DIV+CSS</li>
<li>JQuary</li>
</ul>
</div>
<div>
<p>后台脚本</p>
<ul>
<li>PHP</li>
<li>ASP.net</li>
<li>JSP</li>
</ul>
</div>
<div>
<p>前端框架</p>
<ul>
<li>Extjs</li>
<li>Esspress</li>
<li>YUI</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>三、border
1.border
.demo1 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid #000;
position: absolute;
left: calc(50% - 50px);
top: calc(50% - 50px);
border-radius: 50px; /*圆角:相对于宽而言的*/
}border-radius拆分
border-radius: 10px 20px 30px 40px;
/*左上-右上-右下-左下*/
border-radius: 10px 40px;
/*左上右下--右上左下*/
border-radius: 10px 20px 30px;
/*中间代表两个方向:右上左下*/继续拆分
border-top-left-radius: 10px;
border-top-right-radius: 20px;
border-bottom-right-radius: 30px;
border-bottom-left-radius: 40px;
/*等价*/
border-top-left-radius: 10px 10px;
border-top-right-radius: 20px 20px;
border-bottom-right-radius: 30px 30px;
border-bottom-left-radius: 40px 40px;1/4 圆
/*必须正方形的width=border-top-left-radius:100px 100px*/半圆
/*长方形宽大一倍*/
.demo2 {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid #000;
position: absolute;
left: calc(50% - 50px);
top: calc(50% - 50px);
border-top-left-radius: 100px 100px;
border-top-right-radius: 100px 100px;
}叶子模型
.demo {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid #000;
position: absolute;
left: calc(50% - 50px);
top: calc(50% - 50px);
background-color: green;
border-top-left-radius: 100px 100px;
border-bottom-right-radius: 100px 100px;
}新写法
border-radius: 10px 20px 30px 40px / 10px 20px 30px 40px;2.box-shallow
外阴影&&内阴影
body{
background-color: #000;
}
div{
position: absolute;
left: calc(50% - 50px);
top: calc(50% - 50px);
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: transparent;
border: 1px solid #fff;
不写就是外阴影
box-shadow: 0px 0px 0px 10px #0ff;/*水平偏移量 垂直偏移量 模糊范围(基于原来边框位置向边框两边同时模糊) 传播距离(水平垂直同时增加10) 阴影颜色 */
内阴影
/*box-shadow: inset 1px 0px 5px 0px #fff;*/
内外阴影
/*box-shadow: 0px 0px 10px #fff,inset 0px 0px 10px #fff;*/
/*四边不同颜色模糊实现*/
box-shadow: inset 0px 0px 10px #fff,
3px 0px 10px #f0f,
0px -3px 10px #0ff,
-3px 0px 10px #00f,
0px 3px 10px #ff0;
/*关于Z轴覆盖,哪个阴影先设置,谁就在上*/
}3 个 demo
DEMO1
body {
background-color: #000;
}
div {
position: absolute;
left: calc(50% - 150px);
top: calc(50% - 150px);
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid #fff;
border-radius: 50%;
box-shadow: inset 0px 0px 50px #fff, inset 10px 0px 80px #f0f,
inset -10px 0px 80px #0ff, inset 10px 0px 300px #f0f,
inset -10px 0px 300px #0ff, 0px 0px 50px #fff, -10px 0px 80px #f0f, 10px 0px
80px #0ff;
}太阳
body {
background-color: #000;
}
div {
position: absolute;
left: calc(50% - 25px);
top: calc(50% - 25px);
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background-color: #fff;
border-radius: 50%;
box-shadow: 0px 0px 100px 50px #fff, 0px 0px 250px 125px #ff0;
}DEMO3
div {
position: absolute;
border-radius: 5px;
left: calc(50% - 50px);
top: calc(50% - 50px);
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #fff;
box-shadow: 0px 1px 2px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
transition: all 0.6s;
}
div::after {
content: "";
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
border-radius: 5px;
box-shadow: 0px 5px 15px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3);
opacity: 0;
transition: all 0.6s;
}
div:hover::after {
opacity: 1;
}
div:hover {
transform: scale(1.25, 1.25);
}注意:背景颜色在阴影下面,文字在阴影上面
3.border-image
div {
position: absolute;
left: calc(50% - 50px);
top: calc(50% - 50px);
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 10px solid black;
/*支持渐变色*/
border-color: lightpink;
border-image-source: linear-gradient(red, yellow);
/* 实现背景颜色渐变 */
/* border-image-source: url(.//border.png);
实现边框用背景图片渐变渲染
*/
border-image-slice: 10;
}关于 slice(截取)
div {
position: absolute;
left: calc(50% - 50px);
top: calc(50% - 50px);
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 100px solid black;
border-color: lightpink;
border-image-source: url(.//border.png);
border-image-slice: 100;
/* border-image-slice: 100 50 100 100; */
/* 上右下左 */
/*slice不填的话,默认100%*/
border-image-repeat: stretch;
}几个附加值
div {
position: absolute;
left: calc(50% - 50px);
top: calc(50% - 50px);
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 100px solid black;
border-color: lightpink;
border-image-source: url(.//border.png);
border-image-slice: 100;
/* 让背景图片往外延伸 */
border-image-outset: 100px;
border-image-width: 1; /* border里面能显示图片背景的宽度 */
/* 默认为1,不同于 border-width */
border-image-width: auto; /* 相当于slice + px */
/* border-image-slice: 100 100 fill; */
/* fill填充内容区 */
border-image-slice: 100 100;
}repeat
div {
position: absolute;
left: calc(50% - 50px);
top: calc(50% - 50px);
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 100px solid black;
border-color: lightpink;
border-image-source: url(.//border.png);
border-image-slice: 100 100 fill;
border-image-repeat: round;
/* stretch默认值:拉伸
round:平铺
repeat:平铺
space:平铺
*/
border-image-repeat: round stretch;
/*也可以两个:水平垂直*/
}另一种写法:border-image:source slice repeat;
border-image: url(source/red.png) 100 repeat;四、background
渐变颜色生成器:linear-gradient(); radial-gradient();
div {
position: absolute;
left: calc(50% - 100px);
top: calc(50% - 100px);
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
/* background-image: linear-gradient(#0f0, #f00); */
/* linear-gradient只能当成背景图片来使用,background-color不好使 */
/*两张图片在一个容器中展示*/
background-image: url() url(); /* 可以添加多个背景图片 */
background-size: 100px 200px, 100px 200px;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: 0 0, 100px 0;
}容错机制:容错背景图片展示
1.background-origin:
图片从哪里起始
没规定在哪结束,就开始重复图片 repeat,这就是为什么看起来像是 border-box 开始的
div {
position: absolute;
left: calc(50% - 100px);
top: calc(50% - 100px);
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
padding: 20px;
border: 20px solid transparent;
background-image: url(.//source/pic1.jpeg);
background-origin: padding-box;
/* border-box padding-box(默认值) content-box */
background-repeat: no-repeat;
}background-position 由 background-origin 决定的。position 相对于 origin 定位。
2.background-clip
背景图片从哪块开始截断,从哪块以外的部分都不显示背景图片,即从哪块结束
background-clip: border-box;
/* border-box(默认,废弃值) padding-box content-box text */text 精解:文字内容区反切背景图片
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
div:hover {
background-position: center center;
}
div {
position: absolute;
left: calc(50% - 200px);
top: 100px;
height: 100px;
line-height: 100px;
font-size: 80px;
width: 400px;
background-image: url(.//source/pic2.jpeg);
-webkit-background-clip: text;
/* 固定写法三件套,配合background-clip */
background-clip: text;
-webkit-text-fill-color: transparent;
text-fill-color: transparent;
background-position: 0 0;
transition: all 0.6s;
}3.background-repeat
div {
position: absolute;
left: calc(50% - 100px);
top: calc(50% - 100px);
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
padding: 20px;
background-image: url(.//source/pic4.jpeg);
background-size: 50px 50px;
/* background-repeat: no-repeat; */
/* background-repeat: repeat-x; */
/* background-repeat: repeat-y; */
/* background-repeat: round;深到一定程度蹦进来一张图 */
/* background-repeat: space;空白填充,冲到一定程度填充一张图片 */
/* background-repeat: round space;分别是x,y */
/* background-repeat:repeat-x相当于repeat-x no-repeat; */
}4.background-attachment
改变定位属性的
div {
width: 500px;
height: 700px;
border: 1px solid red;
/* overflow: hidden; */
overflow: scroll;
background-image: url(.//source/pic6.jpeg);
background-size: 300px 300px;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: 100px 100px;
/* background-attachment: local; */
/* 相对于内容区定位 */
/* background-attachment: scroll;默认 */
/* 默认scroll:相对于容器定位 */
/* background-attachment: fixed; */
/* 相对于真正的可视区视口定位 */
}5.background-size
div {
width: 500px;
height: 700px;
border: 1px solid red;
overflow: scroll;
background-image: url(.//source/pic6.jpeg);
background-size: 300px 300px;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
/* contain不改变宽高比,让容器包含一张完整图片,即便会出现repeat
cover填充满容器,不改变宽高比 */
background-attachment: scroll;
}效果
contain(可能 repeat):一条边对齐,另一条小于等于容器另一条
cover(可能超出):一条边对齐,另一条大于等于容器另一条
渐变生成器
linear-gradient
div {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
/* background-image: linear-gradient(red, white);
background-image: linear-gradient(to right, red, green);
background-image: linear-gradient(to left, red, green);
background-image: linear-gradient(to bottom, red, green);
background-image: linear-gradient(to top, red, green);
background-image: linear-gradient(to top right, red, green); */
/* background-image: linear-gradient(0deg, red, green);90deg 180deg */
/* background-image: linear-gradient(90deg, red, 20px, green);颜色的终止位置 */
/* background-image: linear-gradient(90deg, red 20px, green 60px); */
}镜像放射 radial-gradient()
div {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
/* background-image: radial-gradient(red, green, #0ff); */
/* background-image: radial-gradient(red 20%, green 50px, #0ff 40%); */
/* background-image: radial-gradient(circle at 100px 0px, red, green, #0ff); */
/* background-image: radial-gradient(ellipse at 20px 30px, red, green, #0ff); */
/* 放射半径 */
/* closest-corner
closest-side
farthest-corner
farthest-side */
/* background-image: radial-gradient(ellipse farthest-corner at 50px 50px, red, green, #0ff); */
}颜色
HSL
HSLA
currentColor 中转颜色
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border-width: 1px;
border-style: solid;
color: red; /*border竟然颜色改变了。一旦不设置border-color的时候,会继承color,currentColor作为中转*/
/* css1 css2 border-color:color currentColor*/
border-color: currentColor;
}五、text
1.text-shadow
x, y, blur, color
div {
position: absolute;
left: calc(50% - 350px);
top: 100px;
width: 700px;
height: 100px;
font-size: 80px;
text-shadow: 3px 3px 3px #000;
text-shadow: 3px 3px 3px #000, -10px -10px 3px #30f;
}demo
浮雕效果
body {
background-color: #0ff;
}
div {
position: absolute;
left: calc(50% - 350px);
top: 100px;
width: 700px;
height: 100px;
font-size: 80px;
color: #ddd;
text-shadow: 1px 1px #000, -1px -1px #fff;
}镂刻效果
body {
background-color: #0ff;
}
div {
position: absolute;
left: calc(50% - 350px);
top: 100px;
width: 700px;
height: 100px;
font-size: 80px;
color: #ddd;
text-shadow: -1px -1px #000, 1px 1px #fff;
}阴影加强
body {
background-color: #000;
}
div {
position: absolute;
left: calc(50% - 350px);
top: 100px;
width: 700px;
height: 100px;
font-size: 80px;
color: #ddd;
text-shadow: 0px 0px 10px #0f0, 0px 0px 20px #0f0, 0px 0px 30px #0f0;
transition: all 0.3s;
}
div:hover {
text-shadow: 0px 0px 10px #f00, 0px 0px 20px #f10, 0px 0px 30px #f20;
}
div::before {
content: "NO ";
opacity: 0;
text-shadow: 0px 0px 10px #f00, 0px 0px 20px #f10, 0px 0px 30px #f20, 0px -5px
20px #f10, 0px -10px 20px #f20, 0px -15px 30px #f10;
transition: all 3s;
}
div:hover::before {
opacity: 1;
}死神来了
body {
/* background-color: #000; */
}
div {
position: absolute;
left: calc(50% - 350px);
top: 100px;
width: 400px;
height: 150px;
font-size: 100px;
font-weight: bold;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: -400px -50px;
background-image: url(.//source/eye.jpeg);
background-size: 400px 300px;
-webkit-background-clip: text;
background-clip: text;
-webkit-text-fill-color: transparent;
text-fill-color: transparent;
transition: all 3s;
/* text-shadow: 10px 10px 3px #000;
这个不能展现效果?阴影跑到了文字内容上面,因为background-clip:text,文字就变成了背景的一部分
*/
text-shadow: 10px 10px 3px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
div:hover {
background-position: 0 -50px;
}分身
body {
background-color: #000;
}
div {
position: absolute;
left: calc(50% - 350px);
top: 100px;
width: 500px;
height: 150px;
font-size: 60px;
font-weight: bold;
color: #f10;
text-shadow: 0px 0px 5px #f10, 0px 0px 10px #f20, 0px 0px 15px #f30;
transition: all 1.5s;
}
div:hover {
text-shadow: 10px -10px 10px #f00, 10px 10px 15px #ff0;
}描边效果 stroke
div {
position: absolute;
left: calc(50% - 350px);
top: 100px;
width: 500px;
height: 150px;
font-size: 80px;
font-weight: bold;
-webkit-text-stroke: 2px red;
}字体描边效果 stroke
div {
position: absolute;
left: calc(50% - 350px);
top: 100px;
width: 500px;
height: 150px;
font-size: 100px;
font-weight: bold;
color: transparent;
font-family: simsun;
-webkit-text-stroke: 1px red;
}font-face 字体包使用方法
@font-face {
font-family: 'abc';字体包名字
src: url();
}
div {
font-family: 'abc';引入字体包
}引入很多图片格式的原因:
字体格式
- TureType 微软 苹果 .ttf
- opentype 微软 adobe 。opt
- woff .woff
ie .eath5 svg
MIME 协议(.ttf .txt .pdf)
如果不认识,format 让浏览器加强对字体格式的认识。format 产生映射
2. text 系列
white-space
div{
white-space:pre;原封不动的保留你输入时的状态,空格、换行都会保留,并且当文字超出边界时不换行
white-space:nowarp:强制所有文本在同一行内显示。
}word-break
div {
width: 200px;
border: 1px solid black;
/* word-break: keep-all; */
/* 不换行 */
/* word-break: break-all; */
/* 强制换行 */
/* word-break: break-word; */
/* 尽可能保留英文单词完整性 */
}columns 报纸布局
div {
/* columns: column-width||column-count;; */
/* columns: 300px 4; */
column-count: 3;
column-gap: 30px;
/* 空隙 */
column-rule: 1px solid black;
/* 空隙分割线 */
}
p {
margin: 10px 0;
column-span: all;默认1
/* 横穿整个列 */
}-webkit-column-break-before: always;
/* 前面断列,另起一列 */
-webkit-column-break-after: always;
/* 后面断列,另起一列 */column-with
/* column-count: 3;自适应 */
column-width: 300px;
/* 不太准,会自适应 */瀑布流布局 :他尽量让高的成为多数的。一个一个试试就试出来了
div {
/*内部机制不适宜瀑布流布局 */
column-count: 4;
column-rule-style: solid;
}column 应用:小说阅读
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
div {
width: 300px;
height: 500px;
border: 1px solid red;
}
.content {
column-width: 300px;
column-gap: 20px;
border: none;
transition: all 2s;
}
div:hover .content {
transform: translateX(-320px);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="content">
红星资本局从国家药监局官网获悉,1月
14日,国家药监局发布《关于注销酚酞片和酚酞含片药品注册证书的公告(2021年
第6号)》,公告称,根据《中华人民共和国
药品管理法》第八十三条规定,国家药品监督管理局
组织对酚酞片和酚酞含片进行上市后评价,评价认为酚
酞片和酚酞含片存在严重不良反应,在我国使用风险大于
益,决定自即日起停止酚酞片和酚酞含片在我国的生产、销
售和使用,注销药品注册证书(药品批准文号)。
红星资本局从国家药监局官网获悉,1月
14日,国家药监局发布《关于注销酚酞片和酚酞含片药品注册证书的公告(2021年
第6号)》,公告称,根据《中华人民共和国
药品管理法》第八十三条规定,国家药品监督管理局
组织对酚酞片和酚酞含片进行上市后评价,评价认为酚
酞片和酚酞含片存在严重不良反应,在我国使用风险大于
益,决定自即日起停止酚酞片和酚酞含片在我国的生产、销
售和使用,注销药品注册证书(药品批准文号)红星资本局从国家药监局官网获悉,1月
14日,国家药监局发布《关于注销酚酞片和酚酞含片药品注册证书的公告(2021年
第6号)》,公告称,根据《中华人民共和国
药品管理法》第八十三条规定,国家药品监督管理局
组织对酚酞片和酚酞含片进行上市后评价,评价认为酚
红星资本局从国家药监局官网获悉,1月
14日,国家药监局发布《关于注销酚酞片和酚酞含片药品注册证书的公告(2021年
第6号)》,公告称,根据《中华人民共和国
药品管理法》第八十三条规定,国家药品监督管理局
组织对酚酞片和酚酞含片进行上市后评价,评价认为酚
酞片和酚酞含片存在严重不良反应,在我国使用风险大于
益,决定自即日起停止酚酞片和酚酞含片在我国的生产、销
售和使用,注销药品注册证书(药品批准文号)红星资本局从国家药监局官网获悉,1月
14日,国家药监局发布《关于注销酚酞片和酚酞含片药品注册证书的公告(2021年
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>jQuery 实现左右滑屏,(按钮),之前所讲知识完美融合
滑动——slide 插件
六、box
1.IE6 混杂模式盒子
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
border: 10px solid black;
padding: 10px;
/* 触发 */
box-sizing: border-box;
/*默认content-box*/
}
/*
原来:boxWidth=width+border*2+padding*2;
怪异:boxWidth=width
contentWidth=width - border*2 - padding*2
*/宽度不固定,内边距 padding 固定
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
.wrapper {
width: 100%;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid black;
}
.content:first-of-type {
float: left;
width: 50%;
height: 100px;
background-color: yellow;
padding: 0 10px;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.content {
float: left;
width: 50%;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="content"></div>
<div class="content"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>输入框宽度不固定,内边距固定
<style>
.wrapper {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid black;
}
input {
width: 100%;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
/* input天生带2px的border,解决就用怪异盒子 */
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<input type="text">
</div>
</body>产品需求接受形式
input {
width: 300px;
height: 50px;
box-sizing: border-box;
padding: 0 10px;
}宽度用户自定,后端传的,padding border 固定
.wrapper {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid red;
}
.content {
box-sizing: border-box;
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid #fff;
background-color: black;
}<div class="wrapper">
<div class="content"></div>
<div class="content"></div>
<div class="content"></div>
</div>两个值
1.overflow
.wrapper {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid red;
/* overflow: scroll; */
/* 除了当overflow-x,overflow-y之一设置了非 visible时,另一个属性会自动将默认值visible设置为auto */
overflow-x: scroll; /* 就会overflow-y:auto */
}移动端
明星左右滑动模块
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
.wrapper {
width: 300px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid black;
overflow-x: scroll;
overflow-y: auto;
}
/* 最外层溢出部分隐藏,里面盒子=图片总体宽度 */
.box {
width: 800px;
height: 100px;
}
img {
float: left;
display: inline;
width: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="box">
<img src="./1.jpg" alt="" />
<img src="./1.jpg" alt="" />
<img src="./1.jpg" alt="" />
<img src="./1.jpg" alt="" />
<img src="./1.jpg" alt="" />
<img src="./1.jpg" alt="" />
<img src="./1.jpg" alt="" />
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>2.resize 调节元素大小 :会导致重排和重绘,性能消耗
.wrapper {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid red;
/* resize: both; */
/* resize: vertical;竖直 */
overflow: scroll;
}2.flex 弹性盒子
https://note.youdao.com/ynoteshare1/index.html?id=34a5c74103899550601b58d9d10141de&type=note
https://note.youdao.com/ynoteshare1/index.html?id=4be5892bd2084821fe6671d7a4e09e1a&type=note
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
.wrapper {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid black;
display: flex;
/* display: inline-flex; */
flex-direction: row;
/* 默认主轴水平方向,自左向右 */
flex-direction: column;
/* 垂直 */
flex-direction: row-reverse;
/* 逆反 */
flex-direction: column-reverse;
/* 垂直逆反 */
}
.content {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid green;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="content">1</div>
<div class="content">2</div>
<div class="content">3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>换行实现:
flex-wrap
justify-content:基于主轴对齐方式
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
.wrapper {
width: 600px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid black;
display: flex;
flex-direction: nowrap;
/* justify-content: flex-start;默认 */
/* justify-content: flex-end; 主轴向右*/
/* justify-content: center; */
/* justify-content: space-between; */
/* 两边站住,中间自适应 */
/* justify-content: space-around; */
/* 元素元素之间间距相等 */
}
.content {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid green;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="content">1</div>
<div class="content">2</div>
<div class="content">3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>align-items 垂直方向
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
.wrapper {
width: 600px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid black;
display: flex;
flex-direction: nowrap;
/* align-items: baseline; */
/* 基于文字对齐 */
/* align-items: stretch默认; */
/* 未设置内容区高度的话,实现拉伸;如果设置了,就不好使了 */
/* align-items: flex-start; */
/* align-items: flex-end; */
/* align-items: center; */
}
.content {
width: 100px;
/* height: 100px; */
border: 1px solid green;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.content:first-of-type {
/* margin-top: 10px; 验证baseline*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="content">1</div>
<div class="content">2</div>
<div class="content">3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>单行居中
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
.wrapper {
width: 600px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid black;
display: flex;
flex-direction: wrap;
align-items: center; /* 主要针对单行元素来处理对齐方式的 */
align-content: center; /* 必须作用于多行元素 */
justify-content: center;
}
.content {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid green;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="content">1</div>
<div class="content">2</div>
<div class="content">3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>align-content 看官方文档自学
以上都是设置在父级上的
以下是子级
order 相当于 z-index,默认 0,最好添负值;小的在前
.wrapper {
width: 600px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid black;
display: flex;
flex-direction: nowrap;
align-items: stretch;
flex-wrap: wrap;
}
.content {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid green;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.content:first-of-type {
order: -2;
}
.content:nth-of-type(2) {
order: -1;
}align-self
听从自己
.wrapper {
width: 600px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid black;
display: flex;
flex-direction: nowrap;
align-items: center;
flex-wrap: wrap;
}
.content {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid green;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.content:first-of-type {
align-self: flex-start;
}
.content:nth-of-type(2) {
align-self: flex-end;
}强于 align-items(父级),弱于 align-content(父级)
.wrapper {
width: 600px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid black;
display: flex;
flex-direction: nowrap;
align-content: center;
flex-wrap: wrap;
}
.content {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid green;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.content:first-of-type {
align-self: flex-start;
}
.content:nth-of-type(2) {
align-self: flex-end;
}弹性盒子之弹性
flex-grow
当这一行还有剩余空间的时候,按照比例分配剩余空间,最终调整大小
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
.wrapper {
width: 600px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid black;
display: flex;
}
.content {
/* */
/* flex-grow: 1; */
/* 默认0 伸展开了 */
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid green;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.content:first-of-type {
flex-grow: 1;
}
.content:nth-of-type(2) {
flex-grow: 2;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="content">1</div>
<div class="content">2</div>
<div class="content">3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>flex-shrink 默认 1
超出,不换行,启动压缩
.wrapper {
width: 600px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid black;
display: flex;
}
.content {
flex-shrink: 1;
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
}
/* 压缩加权算法 */
/* 200px * 1 + 200px * 1 + 400px * 3 = 1600px */
/*
200px * 1
--------- * 200px = 25px
1600
*/
.content:nth-of-type(3) {
flex-grow: 3;
width: 400px;
}深入剖析:加边框
得出最终结论:真实内容区大小*shrink + (…)=加权值
flex-basis 相当于 width 权重大于 width
默认 auto
basis 与 width 区别
.wrapper {
width: 600px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid black;
display: flex;
}
.content {
flex-basis: 100px;
/* 根据内容撑开 */
flex-shrink: 1;
/* width: 100px; 覆盖*/
height: 200px;
background-color: #f0f;
/*
元素撑开的话,得出以下结论:
只写basis或者basis>width,代表元素的最小宽度
设置了width并且basis小于width
basis<realWidth<width
*/
}
.content:nth-of-type(2) {
background-color: #ff0;
}
.content:nth-of-type(3) {
background-color: #0ff;
}想换行,加汉字或者设置换行
.wrapper {
width: 600px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid black;
display: flex;
}
.content {
height: 200px;
/* word-break: break-word;可换行,就可以参与压缩了 */
}
.content:nth-of-type(1) {
background-color: #0f0;
flex-basis: 200px;
flex-shrink: 5;
}
.content:nth-of-type(2) {
background-color: #ff0;
flex-basis: 200px;
flex-shrink: 1;
}
.content:nth-of-type(3) {
flex-basis: 400px;
background-color: #0ff;
flex-shrink: 1;
}以上,总结
当你设置宽的时候,如果 basis 设置有值,且小于 width,那么真实的宽的范围在 basis
<realWidth<Width
当你不设置 width 的时候,设置 basis,元素真实的宽 min-width 当不换行内容超过内容区
会撑开容易
无论什么情况,被不换行内容撑开的容器,不会被压缩计算
探究 flex 应用
flex:0 1 auto 默认 因为设置了 flex 后会自动压缩
基本应用
.wrapper { width: 600px; height: 600px; border: 1px solid black; display: flex;
/*flex-wrap: wrap;*/ align-content: flex-start; } .content { background-color:
red; flex: 1 1 auto; width: 250px; height: 250px; }1.实现居中
.wrapper {
resize: both; //配合overflow使用
overflow: hidden;
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid black;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
div.content {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid black;
}2.可动态增加的导航栏
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
.wrapper {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid black;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
}
.item {
flex: 1 1 auto;
height: 30px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 30px;
font-size: 20px;
color: #f20;
border-radius: 5px;
}
.item:hover {
background-color: #f20;
color: #fff;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="item">天猫</div>
<div class="item">淘宝</div>
<div class="item">聚划算</div>
<!-- 无论多少,都等分 -->
</div>
</body>
</html>3.等分布局(4 等分,2 等分,中间可加 margin)
实现中间固定,两边等比例自适应
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
.wrapper {
resize: both;
overflow: hidden;
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
border: 1px solid black;
display: flex;
}
.content {
/* flex: 0 1 auto; 默认*/
flex: 1 1 auto;
/* margin: 0 10px; */
border: 1px solid green;
height: 100px;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.content:nth-of-type(2) {
flex: 0 0 200px; /*中间固定,不能伸不能缩,即0,0,*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="content"></div>
<div class="content"></div>
<div class="content"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>实现中间固定,两边不比例自适应
加上 .content:nth-of-type(3) {
flex: 2 2 auto;
}其中一个固定宽度的布局(固定一个,固定两个)
4.圣杯布局
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
.wrapper {
resize: both;
overflow: hidden;
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid black;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
//align-items:stretch//默认 交叉轴如果没有设置,就拉伸
}
.header,
.footer,
.left,
.right {
flex: 0 0 20%; /*不参与伸缩,占20%*/
border: 1px solid black;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.contain {
flex: 1 1 auto; //把中间内容区噔开
display: flex;
}
.center {
flex: 1 1 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="header">header</div>
<div class="contain">
<div class="left">left</div>
<div class="center">center</div>
<div class="right">right</div>
</div>
<div class="footer">footer</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>5.流式布局
模拟 float 布局
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
.wrapper {
resize: both;
overflow: hidden;
width: 400px;
height: 800px;
border: 1px solid black;
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
align-content: flex-start; //模拟float
}
.content {
width: 100px;
border: 1px solid green;
height: 100px;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="content"></div>
<div class="content"></div>
<div class="content"></div>
<div class="content"></div>
<div class="content"></div>
<div class="content"></div>
<div class="content"></div>
<div class="content"></div>
<div class="content"></div>
<div class="content"></div>
<div class="content"></div>
<div class="content"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>作业:刘德华
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
.wrapper {
background-color: red;
resize: both;
overflow: hidden;
display: flex;
}
.left {
margin-top: 20px;
flex: 0 0 auto;
}
img {
width: 150px;
height: 200px;
}
.right {
flex: 1 1 auto;
margin-left: 40px;
}
em {
color: #fff;
font-size: 30px;
}
p {
margin-top: 20px;
color: #fff;
font-size: 60px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="left">
<img src=".\1.jpg" alt="" />
</div>
<div class="right">
<p>刘德华</p>
<em>演员演员演员演员演员演员演员</em>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>熟能生巧
七、动画
1.transition 过渡动画
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
/* transition: transition-property, transition-duration,transition-timing-function,transition-delay; */
/* transition-property: all; */
/* 第一个监听属性 */
/* transition-property: width, height; */
/* transition-duration: ; */
/* 第二个时间间隔 */
/* transition-timing-function:linear ; */
/* 第三个运动状态 */
/* transition-delay: ; */
/* 第四个延迟 */
transition: width 2s linear 1s;
/* 总共3s,1s后开始宽度增加,增加2s */
/* 添加方式
前两个必须有,后两个默认
*/
}
div:hover {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
}动画 demo
div {
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
opacity: 0.5;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
transition: all 2s;
}
div:hover {
opacity: 1;
top: 100px;
left: 100px;
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
}2.cubic-bezier
div {
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
border: 1px solid red;
border-radius: 10px;
transition: all 1s cubic-bezier(0.5, -1.5, 0.8, 2); /*代表两个坐标点
x:(0,1)
y:都可
*/
}
div:hover {
width: 300px;
}3.animation
@keyframes run {
0% {
/* 0%相当于from */
left: 0;
top: 0;
/* background-color: red; */
}
25% {
left: 100px;
top: 0;
/* background-color: green; */
}
50% {
left: 100px;
top: 100px;
/* background-color: blue; */
}
75% {
left: 0;
top: 100px;
/* background-color: coral; */
}
100% {
/* 100%相当于to */
left: 0;
top: 0;
}
}
@keyframes color-change {
0% {
background-color: red;
}
60% {
background-color: blue;
}
100% {
background-color: black;
}
}
div {
position: relative;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
/* animation: run 4s; */
/* animation: run 4s, color-change 4s;两个动画同时运行 */
/* animation: run 4s cubic-bezier(.5,1,1,1);其实是是每一段的运动状态 */
/* animation: run 4s cubic-bezier(.5, 1, 1, 1) 1s;延迟1s执行动画 */
/* animation: run 4s cubic-bezier(.5, 1, 1, 1) 1s 2; 执行2次动画 */
/* animation: run 4s cubic-bezier(.5, 1, 1, 1) 1s infinite; 死循环 */
/* animation: run 4s cubic-bezier(.5, 1, 1, 1) 1s reverse;倒着走 */
/* animation: run 4s cubic-bezier(.5, 1, 1, 1) 1s 2 alternate;先证者走,在倒着走,意味着次数>=2(单摆) */
}animation-fill-mode:
forwards: 设置对象状态为动画结束时候的状态
backwards:设置对象状态为动画开始时候第一针的状态
both:设置对象状态为动画结束和开始的状态的综合体
太阳月亮 demo——文件夹
4.step 跳转动画
@keyframes change-color {
0% {
background-color: red;
}
25% {
background-color: green;
}
50% {
background-color: blue;
}
75% {
background-color: black;
}
100% {
background-color: #fff;
}
}
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(247, 20, 247);
/* animation: change-color 4s steps(1, end); */
/* 不过度 一步到位 */
/* animation: change-color 4s steps(2, end); */
/* 每一段用2步实现,动画更加细腻了 */
/* animation: change-color 4s steps(1, start); */
/* start与end
end保留当前帧状态,直到这个动画时间结束 忽略最后一针
start保留下一针状态,直到这段动画时间结束 忽略第一针
*/
/* 要想弥补时间段 想看见最后一针
animation: change-color 4s steps(1, end) forwards;
*/
}区别 end 与 start
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
@keyframes run {
0% {
left: 0;
}
25% {
left: 100px;
}
50% {
left: 200px;
}
75% {
left: 300px;
}
100% {
left: 400px;
}
}
.demo1,
.demo2 {
position: absolute;
left: 0;
background-color: black;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
color: #fff;
}
.demo1 {
animation: run 4s steps(1, start);
}
.demo2 {
top: 100px;
/* animation: run 4s steps(1, end); */
animation: run 4s steps(1, end) forwards;
}
/*
steps(1,end);===step-end
steps(1,start);===step-start
*/
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="demo1">start</div>
<div class="demo2">end</div>
</body>
</html>打字效果
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
@keyframes cursor {
0% {
border-left-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);
}
50% {
border-left-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 1);
}
100% {
border-left-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);
}
}
@keyframes cover {
0% {
left: 0;
}
100% {
left: 100%;
}
}
div {
position: relative;
display: inline-block;
height: 100px;
/* background-color: red; */
font-size: 80px;
line-height: 100px;
font-family: monospace;
}
div::after {
content: "";
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 10px;
height: 90px;
width: 100%;
background-color: #fff;
border-left: 2px solid black;
box-sizing: border-box;
animation: cursor 1s steps(1, end) infinite, cover 12s steps(12, end);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>sdknajnakjna</div>
</body>
</html>表盘效果——文件夹
跑马效果
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
@keyframes run {
0% {
background-position: 0 0;
}
100% {
background-position: -2400px 0;
}
}
div {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-image: url(./web/horse.png);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: 0 0;
animation: run 0.3s steps(12, end) infinite;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="horse"></div>
</body>
</html>5.rotate3D 变换
rotate:2d 变换
rotateX,rotateY,rotateZ:3d 变换
旋转
@keyframes round {
0% {
transform: rotate(0deg);
}
100% {
transform: rotate(360deg);
}
}
div {
position: absolute;
left: 200px;
top: 200px;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-image: url(./source/pic6.jpeg);
background-size: cover;
transform: rotate(0deg);
/* transform-origin: center center; */
/* 圆心给谁设置,参考的就是谁 */
transform-origin: 0 0;
animation: round 2s infinite;
}3D 变换
body {
perspective: 800px;
transform-style: preserve-3d;
perspective-origin: 300px 300px;
}
div {
position: absolute;
left: 200px;
top: 200px;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-image: url(./source/pic6.jpeg);
background-size: cover;
transform-origin: 0 0;
/* transform: rotateX(0deg); */
/* transform: rotateX(0deg) rotateY(0deg); */
/* 旋转顺序不同,结果不同 */
}rotate3d()
transform: rotate3d(x, y, z, angle); 矢量和作为旋转轴
小练习图片钟摆效果
body {
perspective: 800px;
transform-style: preserve-3d;
perspective-origin: 300px 300px;
}
@keyframes change {
0% {
transform: rotateX(-45deg) rotateY(90deg);
}
100% {
transform: rotateX(45deg) rotateY(90deg);
}
}
div {
position: absolute;
left: 200px;
top: 200px;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-image: url(./source/pic6.jpeg);
background-size: cover;
transform-origin: 0 0;
animation: change 2s cubic-bezier(0.5, 0, 0.5, 1) infinite alternate;
}6.scale 伸缩
/* transform: scale(1, 2); 2d x,y轴*/
/*
transform: scaleX();
transform: scaleY();
transform: scalez();
transform: scale3d(); 就是叠加
*/
/* scale:
1.伸缩元素变化坐标轴的刻度 ,translateX,Y验证。伸缩之后,translateX(100)产生的效果是200
2.设置两次,则第二次在第一次基础上叠加
3.旋转伸缩在一个轴进行
4.雁过留声 伸缩过的影响一直保留
*/
/* transform: scale() rotate();位置讲究 先后scale不一样*/7.skew 倾斜
skew(x, y);
skewx();
skewy();
demo
body {
perspective: 800px;
transform-style: preserve-3d;
perspective-origin: 300px 300px;
}
@keyframes skewchange {
0% {
transform: skew(45deg, 45deg);
}
50% {
transform: skew(0, 0);
}
100% {
transform: skew(-45deg, -45deg);
}
}
div {
position: absolute;
left: 200px;
top: 200px;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-image: url(./source/pic6.jpeg);
background-size: cover;
transform-origin: center center;
/* transform: skew(0deg, 0deg); */
/* 倾斜的不是元素本身,而是坐标轴
坐标轴倾斜,刻度被拉伸 */
/*
skew(x,y);
skewx()
skewy()
*/
animation: skewchange 4s cubic-bezier(0, 0, 1, 1) infinite alternate;
}8.translate+perspective
2d translate(x, y)
translatex() translatey() translatex() translate3d()
/* transform: translate(100px); */
/* transform: translate3d(100px, 100px 100px); */
/*
transform: translatex()
translatez()
*/
transform: rotatey(90deg) translatez(100px);
transform: translatez(100px) rotatey(90deg);小应用:calc(50% - 0.5*宽高),不知道宽高:
left: 50%;
transform: translatex(-50%) 半个身位;关于 translatez()
body {
perspective: 800px;
}
div {
position: absolute;
left: 200px;
top: 200px;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-image: url(demo/u.png);
background-size: cover;
/*transform: translatez(100px) rotatey(90deg);*/
/*z没起作用?旋转晚了*/
transform: rotatey(90deg) translatez(100px);
}demo
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
:root {
height: 100%;
}
body {
perspective: 800px;
height: 100%; //需要有高度才能实现鼠标移动到哪里都能触发事件
}
.content1,
.content2,
.content3,
.content4,
.content5 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-image: url(./source/pic3.jpeg);
background-size: cover;
position: absolute;
top: 200px;
transform: rotateY(45deg);
}
.content1 {
left: 200px;
}
.content2 {
left: 400px;
}
.content3 {
left: 600px;
}
.content4 {
left: 800px;
}
.content5 {
left: 1000px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="content1"></div>
<div class="content2"></div>
<div class="content3"></div>
<div class="content4"></div>
<div class="content5"></div>
<script>
document.body.onmousemove = function (e) {
this.style.perspectiveOrigin = "" + e.pageX + "px " + e.pageY + "px";
};
</script>
</body>
</html>与 perspective 类似的一个东西:
transform: perspective(800px) rotateY(45deg);
写在前面并且元素本身,眼睛就在 center 不能调
perspective 在父级才有效
景深可以叠加
深入理解 perspevtive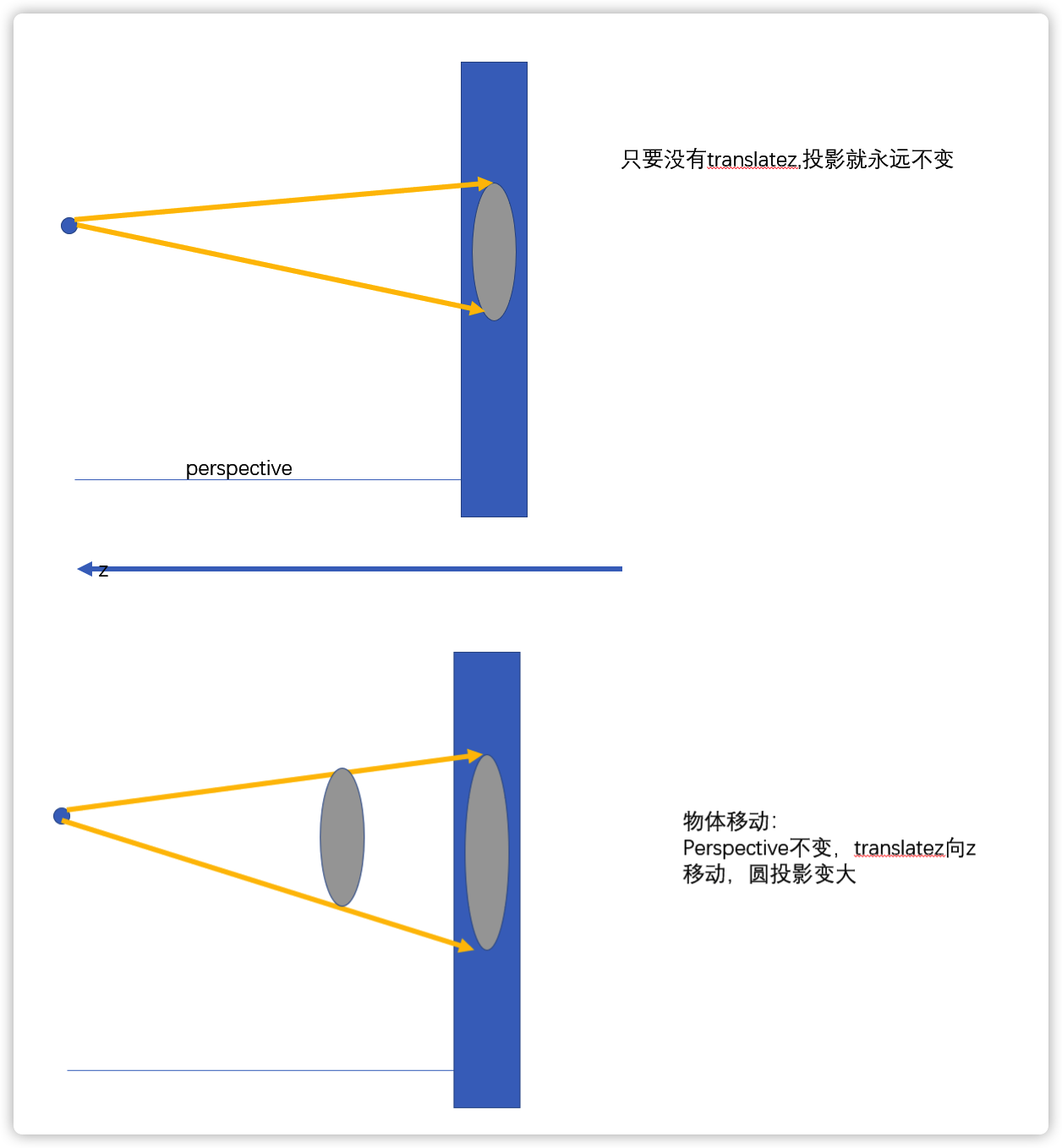
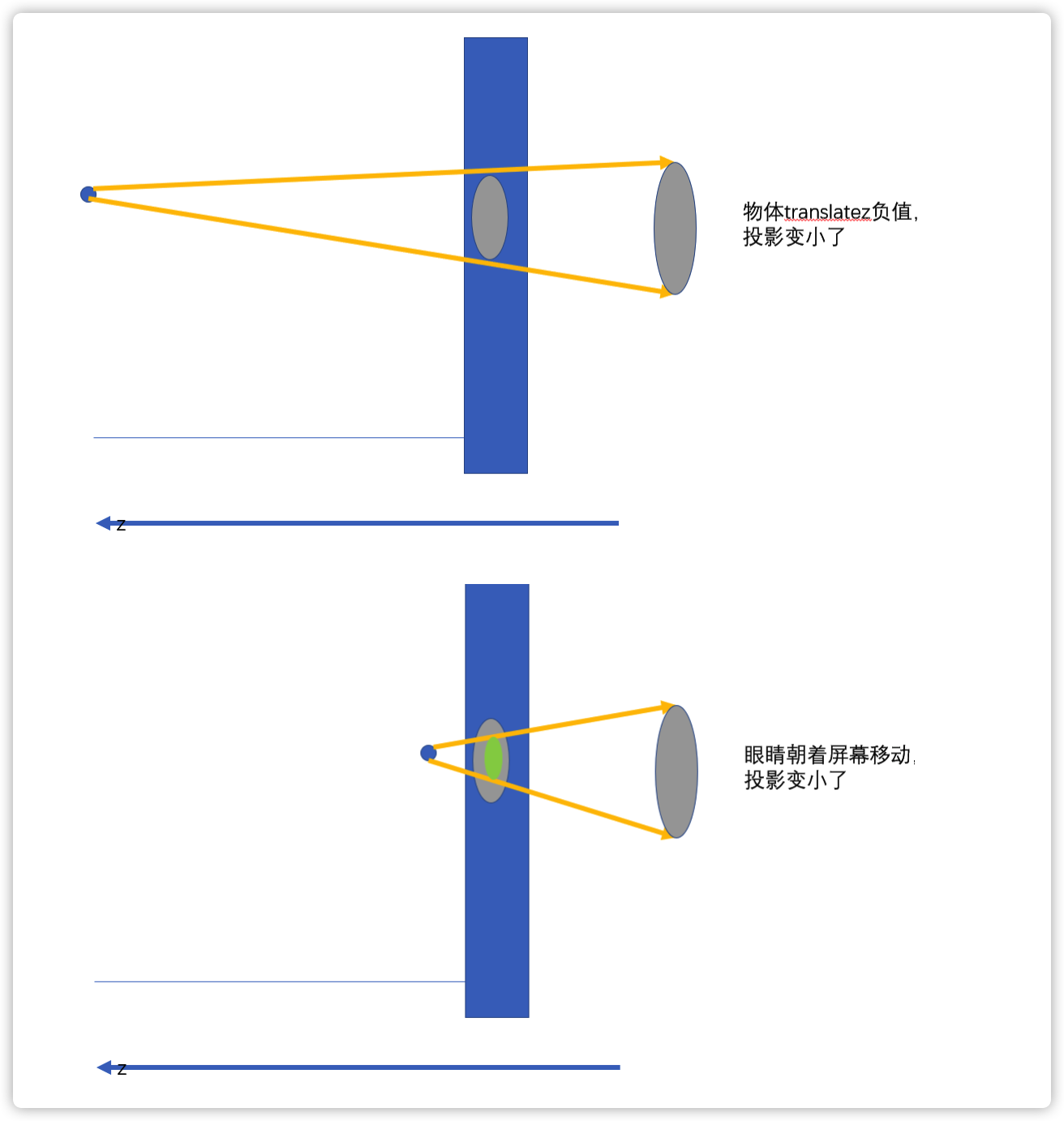
body {
perspective: 800px; /*移动眼睛*/
perspective-origin: 300px 300px;
}
div {
position: absolute;
left: 200px;
top: 200px;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-image: url(demo/u.png);
background-size: cover;
/*移动物体*/
/*transform: translatez(100px);*/
/*快接近800就见不到了,快后脑勺了*/
transform: translatez(100px);
}深入理解 perspective
transform-style
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
body {
perspective: 800px;
perspective-origin: 300px 100px;
}
.wrapper {
position: absolute;
left: 200px;
top: 200px;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: red;
transform: rotateY(0deg);
/*父级旋转会带儿子旋转,因为浏览器渲染不了,所以z轴体现不出来,想立体,给父级(不能祖父)加上transform-style: preserve-3d;*/
}
.demo {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-image: url(demo/u.png);
background-size: cover;
transform: translateZ(100px);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="demo"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>transform-origin
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
body {
perspective: 800px;
perspective-origin: 300px 100px;
transform-style: preserve-3d;
}
@keyframes move {
0% {
transform: rotateY(0deg);
}
100% {
transform: rotateY(360deg);
}
}
div {
position: absolute;
left: 200px;
top: 200px;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-image: url(demo/u.png);
background-size: cover;
animation: move 2s linear infinite;
transform-origin: 100px 100px 100px;
/* 可以设置空间点中心旋转 */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>照片墙
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
:root,
body {
height: 100%;
}
body {
perspective: 3000px;
transform-style: preserve-3d;
/* 一旦设置了这两个属性当中一条,他就变成了定位的参照物元素,所以这里没高度的话就导致没高度了 */
}
@keyframes round {
/*让父级转 简单*/
0% {
transform: translate(-50%, -50%) rotateY(0deg);
}
100% {
transform: translate(-50%, -50%) rotateY(360deg);
}
}
div.wrapper {
position: absolute;
left: calc(50%);
top: calc(50%);
/* 写了top没生效的重要原因:父级没有高度,因为body,解决就把body上面 height打开 */
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
transform-style: preserve-3d;
animation: round 5s linear infinite;
}
img {
position: absolute;
width: 300px;
/* backface-visibility: hidden; */
/* 图片背部 */
}
img:nth-of-type(1) {
transform: rotateY(45deg) translatez(800px);
/*沿着自己的z轴向外拓*/
}
img:nth-of-type(2) {
transform: rotateY(90deg) translatez(500px);
/* 可以改变y值,实现层叠 */
}
img:nth-of-type(3) {
transform: rotateY(135deg) translatez(500px);
}
img:nth-of-type(4) {
transform: rotateY(180deg) translatez(500px);
}
img:nth-of-type(5) {
transform: rotateY(225deg) translatez(500px);
}
img:nth-of-type(6) {
transform: rotateY(270deg) translatez(500px);
}
img:nth-of-type(7) {
transform: rotateY(315deg) translatez(500px);
}
img:nth-of-type(8) {
transform: rotateY(360deg) translatez(500px);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<img src="demo/u.png" alt="" />
<img src="demo/u.png" alt="" />
<img src="demo/u.png" alt="" />
<img src="demo/u.png" alt="" />
<img src="demo/u.png" alt="" />
<img src="demo/u.png" alt="" />
<img src="demo/u.png" alt="" />
<img src="demo/u.png" alt="" />
</div>
<script>
document.body.onmousemove = function (e) {
this.style.perspectiveOrigin = "" + e.pageX + "px " + e.pageY + "px";
};
</script>
</body>
</html>作业:3D 魔方 知识点是一样的
9.matrix
矩阵就是 transform 给咱们选中的计算规则
矩阵函数传的参数是矩阵的前两行
平移// translate
| 1 0 e| |x| |x + e|
| 0 1 f| * |y| = |y + f|
| 0 0 1| |z| |1 |
matrix(1,0,0,1,e,f); === translate(x, y);
// scale
| a,0,0 | | x | | ax |
| 0,d,0 | * | y | = | dy |
| 0,0,1 | | 1 | | 1 |
matrix(a,0,0,d,0,0); === scale(x, y);
// rotate
matrix(cos(θ),sin(θ),-sin(θ),cos(θ),0,0); === rotate(θ);
| cos(θ),-sin(θ),e | | x |
| sin(θ),cos(θ) ,f | * | y |
| 0 ,0 ,1 | | 1 |
x1 = cos(θ)x - sin(θ)y + 0
y2 = sin(θ)x + cos(θ)y + 0
matrix(1,tan(θy),tan(θx),1,0,0)
matrix(1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,x,y,z,1) 缩放
matrix(x,0,0,0,0,y,0,0,0,0,z,0,0,0,0,1) 平移利用矩阵实现镜像:核心是符号取反
div{
width:200px;
height:200px;
background-image:url(source/pic3.jpeg);
background-size: cover;
transform:matrix(-1,0,0,1,0,0);
}
|-1,0, 0 | | x | | -x | x取反,反推第一个矩阵表达式
| 0, 1, 0 | * | y | = | -y |
| 0, 0, 1 | | 1 | | 1 |八、性能优化
CPU 中央处理器,擅长逻辑运算
GPU 显卡,擅长图片绘制,高精度的浮点数运算。{家用,专业},尽量少复杂动画,即少了 GPU,烧性能。
区块链技术(GPU)
- 触发 reflow:
改变窗口大小
改变文字大小
内容的改变,输入框输入文字
激活伪类,如:hover
操作 class 属性
脚本操作 DOM
y 计算 offsetWidth 和 offsetHeight
设置 style 属性:.style….style…—–>.class{}
css3 优化:
在 gpu 层面上操作:改变 opacity 或者 transform:translate3d()/translatez();
最好添加 translatez(0); 小 hack 告诉浏览器告诉浏览器另起一个层
减少重排和重绘
css
1、使用transform 替代top
2、使用visibility 替换display:none ,因为前者只会引起重绘,后者会引发回
流(改变了布局
3、避免使用table布局,可能很小的一个小改动会造成整个table的重新布局。
4、尽可能在DOM树的最末端改变class,回流是不可避免的,但可以减少其影
响。尽可能在DOM树的最末端改变class,可以限制了回流的范围,使其影响
尽可能少的节点。
5、避免设置多层内联样式,CSS选择符从右往左匹配查找,避免节点层级过多。
CSS3硬件加速(GPU加速),使用css3硬件加速,可以让transform、opacity、
filters这些动画不会引起回流重绘。但是对于动画的其它属性,比如
background-color这些,还是会引起回流重绘的,不过它还是可以提升这些动画
的性能。
js
1、避免频繁操作样式,最好一次性重写style属性,或者将样式列表定义为class
并一次性更改class属性。
2、避免频繁操作DOM,创建一个documentFragment,在它上面应用所有DOM
操作,最后再把它添加到文档中。
3、避免频繁读取会引发回流/重绘的属性,如果确实需要多次使用,就用一个
变量缓存起来。
4、对具有复杂动画的元素使用绝对定位,使它脱离文档流,否则会引起父元素
及后续元素频繁回流。新方法:will-change:transform;专门处理 GPU 加速问题
应用:hover 上去后才告诉浏览器要开启新层,点击才触发,总之提前一刻告诉就行
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
div.hover {
will-change: transform;
}
div.active {
transform: scale(2, 3);
}浏览器刷新页面的频率 1s 60s
每 16.7mm 刷新一次
gpu 可以再一帧里渲染好页面,那么当你改动页面的元素或者实现动画的时候,将会非常流畅
- 触发 repaint:
repaint:如果只是改变某个元素的背景色、
文 字颜色、边框颜色,不影响它周围或内部布局的属性
repaint
repaint 速度快于 reflow
浏览器渲染过程:
download html download css download js css rules tree(construct) domAPI domTree
cssrulestree cssomAPI 最终cssomTree domtree cssomTree renderTree | | layout布局
---- > paint喷色 (reflow重构) (repaint) 逻辑图(多层矢量图) ----->
实际绘制(栅格化) 不设置就用cpu绘制 google chrome 自动调用 gpu九、显示器的成像原理
空间混色法 rgb
实质上并排排列(验证)
.wrapper {
display: flex;
}
.demo {
width: 1px;
height: 10px;
}
.demo:nth-of-type(2n) {
background-color: #f00;
/*蓝
}
.demo:nth-of-type(2n+1){
background-color: #00f;
/*红*/
}像素:—>红绿蓝像点—–>空间混色
最小的单位:像点。像素由 3 个像点构成。
空间混色法应用
crt 显示屏
lcd 液晶屏
点距:crt 显示屏求点距的方法的意义,是几乎所有屏幕都通用的
像素的大小:点距
物理像素:设备出厂时,像素的大小
dpi:1 英寸所能容纳的像素点数
1 英寸= 2.54cm
dpi 打印机在一英寸屏幕里面可以打印多少墨点
ppi 一英寸所能容纳的像素点数(点距数)
参照像素
96dpi 一臂之遥的视角去看,显示出的具体大小
标杆 1/96*英寸
css 像素=逻辑像素
设备像素比 dpr = 物理像素/css 像素
衡量屏幕好不好:不看分辨率(分辨率:固定宽高下,展示的像素点数)
看的是 dpi
十、响应式网站开发
1.思考?
用户通过什么来看页面?电脑 (pc 端), 手机 ,平板(移动端) (大小/分辨率)
如何使页面在不同的设备上展示的效果相同的?
不同的设备 开发不同的页面
只需要开发一套页面 让用户在不同的设备(大小或者分辨率如何变化)上看到的页面呈现效果是完美的
手机上像素大,像素点的密集程度变大了
demo
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
div {
font-size: 14px;
}
.wrapper {
width: 1500px;
font-size: 0;
}
.content {
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
border: 1px solid black;
display: inline-block; //不用浮动,而是用这种方法
box-sizing: border-box;
/*
换行?
1.凡是带有inline-block都有文字特性,制表符=文字大小
2.border
*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="content"></div>
<div class="content"></div>
<div class="content"></div>
<div class="content"></div>
<div class="content"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>2.响应式网页设计
响应式网页设计或称自适应网页设计或称回应式网页设计/对应式网页设计,是一种网页设计的技术做法,该设计可使网站在不同的设备(从桌面计算机显示器到移动电话或其他移动产品设备)上浏览时对应不同分辨率皆有适合的呈现,减少用户进行缩放,平移和滚动等操作行为。
真正的响应式设计方法不仅仅是根据可视区域大小而改变网页布局,而是要从整体上颠覆当前网页的设计方法,是针对任意设备的网页内容进行完美布局的一种显示机制。
用一套代码解决几乎所有设备的页面展示问题
设计工作由产品经理或者美工来出
详解 meta:将页面大小 根据分辨率不同进行相应的调节 以展示给用户的大小感觉上差不多
1css 像素 != 设备像素 (根据屏幕分辨率 相应的调整)
<meta
name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, user-scalable=no"
/>
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />3.设置视口
模拟移动端的 meta
<meta
name="viewport"
content="width=device-width,minimum-scale=1.0,maximum-scale=1.0,user-scalable=no"
/>width: 可视区宽度
device-width: 设备宽度
minimum-scale: 最小缩放比
maximum-scale: 最大缩放比
width = device-width : iphone 或者 ipad 上横竖屏的宽度 = 竖屏时候的宽度 不能自适应的问题
initial-scale=1.0 : windows phone ie 浏览器 上横竖屏的宽度 = 竖屏时候的宽度 不能自适应的问题
user-scalable: 是否允许用户缩放
Css 像素根据设备像素进行计算 1css 像素 == 1 是设备像素 根据设备的分辨率 dpi 值来计算 css 像素真正展现的大小
meta 功能即适配各种不同分辨率的设备
4.响应式网页开发方法
- 流体网格:可伸缩的网格 (大小宽高 都是可伸缩(可用 flex 或者百分比来控制大小)float)—》 布局上面 元素大小不固定可伸缩
- 弹性图片:图片宽高不固定(可设置 min-width: 100%)
- 媒体查询:让网页在不同的终端上面展示效果相同(用户体验相同 à 让用户用着更爽) 在不同的设备(大小不同 分辨率不同)上面均展示合适的页面
- 主要断点: 设备宽度的临界点
大小的区别 —》 宽度不同 —》 根据不同宽度展示不同的样式
响应式网页开发主要是在 css 样式(异步加载)上面进行操作
主要断点
5.媒体查询
媒体查询是向不同设备提供不同样式的一种方式,它为每种类型的用户提供了最佳的体验。
css2: media type
media type(媒体类型)是 css 2 中的一个非常有用的属性,通过 media type 我们可以对不同的设备指定特定的样式,从而实现更丰富的界面。
css3: media query
media query 是 CSS3 对 media type 的增强,事实上我们可以将 media query 看成是 media type+css 属性(媒体特性 Media features)判断。
如何使用媒体查询?
媒体查询的引用方法有很多种:
- link 标签
- @import url(example.css) screen and (width:800px);
- css3 新增的@media
媒体查询不占用权重
使用方法
媒体类型(Media Type): all(全部)、screen(屏幕)、print(页面打印或打印预览模式)
媒体特性(Media features): width(渲染区宽度)、device-width(设备宽度)…
Media Query 是 CSS3 对 Media Type 的增强版,其实可以将 Media Query 看成 Media Type(判断条件)+CSS(符合条件的样式规则)
6.媒体类型
逻辑操作符
合并多个媒体属性 and
@media screen and (min-width: 600px) and (max-width: 100px);合并多个媒体属性或合并媒体属性与媒体类型, 一个基本的媒体查询,即一个媒体属性与默认指定的 screen 媒体类型。
指定备用功能
@media screen and (min-width: 769px), print and (min-width: 6in)“没有 or 关键词可用于指定备用的媒体功能。相反,可以将备用功能以逗号分割列表的形式列出
这会将样式应用到宽度超过 769 像素的屏幕或使用至少 6 英寸宽的纸张的打印设备。
指定否定条件
@media not screen and (monochrome);要指定否定条件,可以在媒体声明中添加关键字 not,不能在单个条件前使用 not。该关键字必须位于声明的开头,而且它会否定整个声明。所以,上面的示例会应用于除单色屏幕外的所有设备。
向早期浏览器隐藏媒体查询
media="only screen and (min-width: 401px) and (max-width: 600px)"媒体查询规范还提供了关键字 only,它用于向早期浏览器隐藏媒体查询。类似于 not,该关键字必须位于声明的开头。Only 指定某种特定的媒体类型 为了兼容不支持媒体查询的浏览器
早期浏览器应该将以下语句 media=”screen and (min-width: 401px) and (max-width: 600px)”
解释为 media=”screen”: 换句话说,它应该将样式规则应用于所有屏幕设备,即使它不知道媒体查询的含义。
无法识别媒体查询的浏览器要求获得逗号分割的媒体类型列表,规范要求,它们应该在第一个不是连字符的非数字字母字符之前截断每个值。所以,早期浏览器应该将上面的示例解释为:media=”only”
因为没有 only 这样的媒体类型,所以样式表被忽略。
Query -à css3
易混淆的宽度
device-width/height width/height来做为的判定值。device-width/device-height 是设备的宽度(如电脑手机的宽度 不是浏览器的宽度)
width/height 使用 documentElement.clientWidth/Height 即 viewport 的值。渲染宽度/高度
视口宽度/
7.单位值
Rem:rem 是 CSS3 新增的一个相对单位(root em,根 em)相对的只是 HTML 根元素。
Em:em 是相对长度单位。相对于当前对象内文本的字体尺寸。如当前对行内文本的字体尺寸未被人为设置,则相对于浏览器的默认字体尺寸。
Px: px 像素(Pixel)。相对长度单位。像素 px 是相对于显示器屏幕分辨率而言的。
Vw:相对于视口的宽度。视口被均分为 100 单位的 vw
Vh:相对于视口的高度。视口被均分为 100 单位的 vh
Vmax: 相对于视口的宽度或高度中较大的那个。其中最大的那个被均分为 100 单位的 vmax
Vmin:相对于视口的宽度或高度中较小的那个。其中最小的那个被均分为 100 单位的 vmin
rem 相对于html元素的font-size大小 em 相对于本身的font-size大小
font-size属性是可以继承的 vw/ vh 相对于视口而言的 会把视口分成100份 vmax
区视口宽高中最大的一边分成100份 vmin 区视口宽高中最小的一边分成100份 css样式引入
媒体查询不占用权重8.响应式设计是最佳选择吗?
不是的,内容设计胡问题都可以通过响应式设计思路解决, 项目的预算,目标用户以及定位决定了其实现方式。
项目的预算,人力,物力,财力, 时间成本
目标用户,
产品定位
渐进增强 —》 iphone6 向上兼容 兼容最新设备
优雅降级 —》 开发通用版本 再兼容老版本 向下兼容
先移动端 —》 pc 端
先 iphone6 为初始原型 开发 —》 兼容其他的设备 ====》 渐进增强



